Monday, September 30, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Breeding population of Terns and Western Reef Hero...
Lupine Publishers: Breeding population of Terns and Western Reef Hero...: Lupine Publishers- Environmental and Soil Science Journal Abstract The research was conducted on Ghabre Nakhoda and Dara islands in ...
Friday, September 27, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Incidence of Patella Alta in A...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Incidence of Patella Alta in A...: Lupine Publishers | Journal of Orthopaedics Abstract Background: Altered patellar alignment is associated with anterior kn...
Thursday, September 26, 2019
Lupine Publishers: A Case Study of an Environmental Project Evaluatio...
Lupine Publishers: A Case Study of an Environmental Project Evaluatio...: Lupine Publishers- Environmental and Soil Science Opinion This paper presents carried out work on the realization pat...
Monday, September 23, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publiahers | Radiocarpal Dislocation-a Comp...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publiahers | Radiocarpal Dislocation-a Comp...: Lupine Publishers | Journal of Orthoipaedics Abstract Go to The volar shearing distal radius fractures associated with subluxation...
New Clinical Initiatives at the Steno Diabetes Center Odense and in the Region of Southern Denmark
Diabetes Open access Journals- Lupine Publishers
Abstract
In general, patients with diabetes still have an increased mortality
risk, increased risk of micro- and macro-vascular complications
and a decreased quality of life. Despite better options for treatment
and care, to many diabetes patients are still not in optimized
treatment control in order to avoid complications. In Denmark there is a
long tradition for focused diabetes treatment and care,
as well as research and manufacturing insulin and other
antihyperglycemic drugs. Five Steno Diabetes Centers, one in each region
of Denmark, have emerged as a part of the Danish Health Care System. The
overall aim for these centers is to provide optimized
treatment and care for all patients with diabetes regardless of age,
type of diabetes, co-morbidity and where in the Health Care
System the patient is treated. The vision is to provide treatment,
research and education at the highest international level in the
future. Steno Diabetes Center Odense is a new diabetes center which will
attempt to realize this aim and vision for patients with
diabetes and health care professionals in the Region of Southern
Denmark. In this paper we describe the present and forthcoming
new clinical initiatives at Steno Diabetes Center Odense and at its
partner hospitals in the Region of Southern Denmark, which is
planned or in the process of implementation.
Introduction
The Danish physician Hans Christian Hagedorn (1888-1971)
initiated the industrial production of insulin in Denmark in 1923
together with the Danish physiologist August Krogh (1874-1949)
by founding the company Nordisk Insulin Laboratorium, which
much later merged into the pharmaceutical company Novo Nordisk
A/S [1]. Further in 1936, Hans Christian Hagedorn co-discovered
the principle of addition of protamine to insulin, in order to protract
its time of action [2]. This principle has been marketed and in use
since 1946, known as Neutral Protamine Hagedorn insulin (NPH
insulin). The initial idea of Nordisk Insulin Laboratorium was to
ensure the availability of insulin for the patients, and to support
research, treatment and care of patients with diabetes. Thus, Hans
Christian Hagedorn founded Steno Memorial Hospital in 1932,
a private-based hospital solely for treatment and care of patients
with diabetes. In 2017, Steno Memorial Hospital, now called Steno
Diabetes Center Copenhagen, was entrusted from Novo Nordisk
A/S to the National Danish Health Care System, for future treatment
and care of patients with diabetes in the Capital Region of Denmark.
At the same time, the Novo Nordisk Foundation granted a donation
of approximately 1 billion euros to support the foundation and
development of similar Steno Diabetes Centers in the other four
regions of Denmark, thus covering the entire Denmark with
specialized centers within prevention, treatment, care and research
in diabetes. During 2018, four diabetes centers have been formed:
Steno Diabetes Center Odense (SDCO), Steno Diabetes Center Århus
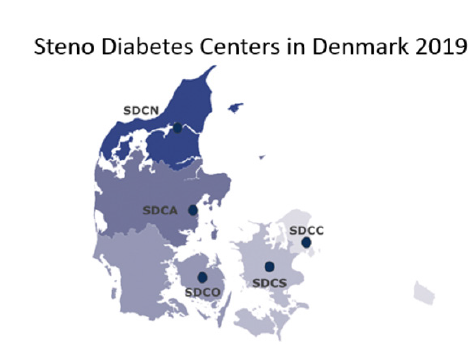
(SDCA), Steno Diabetes Center of Northern Jutland (SDCN) and
Steno Diabetes Center Zeeland (SDCS)(Figure 1). All centers are
attached to general hospitals in which most other specialties are
present. The grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation also covers
new buildings, which will be built and specially designed to future
management of diabetes care and treatment, comprising treatment
of both children and adults, in addition to diabetes research and
education of health care professionals.
Steno Diabetes Center Odense
SDCO was founded January 1st, 2018 and is currently taking
care of approximately 3200 patients with all kinds of diabetes.
The four core activities of SDCO are: prevention and treatment
of diabetic complications, clinical research, education of health
care professionals and cross-sectorial collaboration between the
different health care sectors. The overall aim is to provide the
highest international level of treatment, care and research within
diabetes, in order to give patients with diabetes in the future a lifespan and quality of life not different from the population
without diabetes. SDCO will have the overall responsibility for the
quality and treatment and care of patients with diabetes for the
whole diabetes population of the Region of Southern Denmark,
which is currently approximately 56.000 patients with diabetes [3],
regardless of where the individual patient is treated (hospitals, outpatient
clinics, primary health care providers etc).
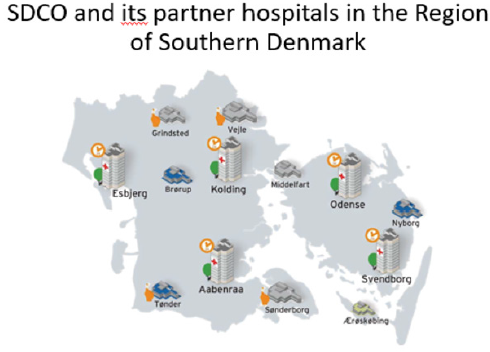
To obtain the goal of ensuing and increasing the quality of
patient care and treatment a close collaboration between SDCO,
SDCO partner hospitals, communities and primary health care
providers has to be reinforced and further developed (Figure 2). In
addition to current standard treatment of patients with diabetes,
numerous additional new clinical and non-clinical activities and
projects will be developed and implemented within the next ten
years. The standard care and treatment activities will be continued
within the Regional budget, whereas the new additional activities
will be covered within the grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation.
Steno Diabetes Center Odense
The aim of the new clinical initiatives is to add on to the current
standard management of patient care and treatment at the center
and its partner hospitals, and thus to improve the overall quality
of patient care and treatment for all patients with diabetes in the
future in the Region of Southern Denmark.
Definition of a Clinical Initiative
The new initiatives as defined in the screenplay for SDCO
is a time-limited project described in detail in a specific project
description, which has to be approved in advance by the board of
SDCO. Thus, the initiative runs into different phases: preparation
of synopsis-approval by the board-preparation of detailed project
description-approval by the board-detailed planning-initiation and
implementation in the clinic-completion of the project-evaluationfinal
decision to continue or not as standard care. Overall the project
continues for three years. Based on evaluation of key parameters it
is decided whether the initiative will continue as future standard
management in the clinic or not.
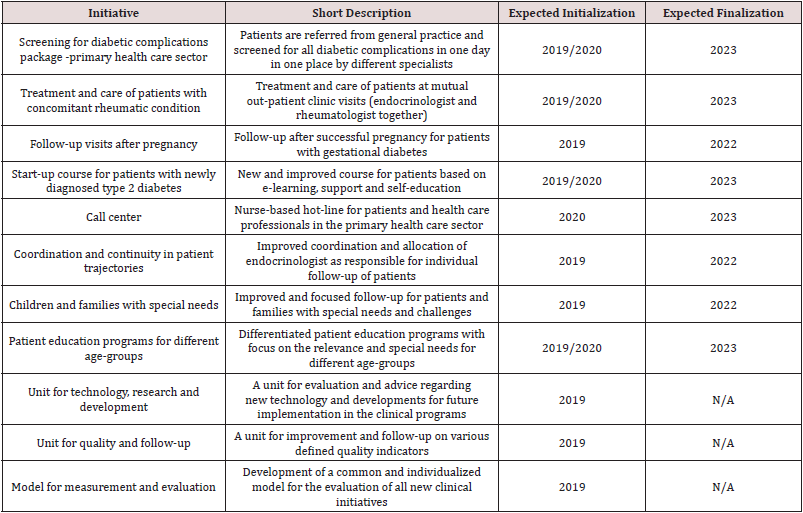
Approved Clinical Initiatives at SDCO Under or Awaiting Implementation
Adults with Diabetes: Table 1 gives an overview of the various
clinical initiatives which have been planned, approved and initiated
from 2018 until the present date at SDCO and, for some initiatives,
at the partner hospitals in the Region of Southern Denmark.
Table 1: New approved clinical initiatives from the Steno Diabetes Center Odense for patients with diabetes from 2018-19 and status
of implementation in the clinic.


Extended Opening Hours: The extended opening hours
late afternoon every week gives patients with full-time work the
possibility to have appointments in the clinic outside their working
hours. In this initiative there is also an option to have acute
appointments at the out-patient clinic according to the need. Thus,
patients with dysregulated diabetes or newly diagnosed patients
without ketoacidosis admitted to the emergency ward, do have the
option to have an appointment the following day at SDCO.
Diabetes Psychologist: The American Diabetes Association
guidelines for the management of diabetes [4] recommend that
psycho-social support should be an integrated part of diabetes
care and should be offered. Some evidence support this notion, and
that psychologic intervention can result in increased acceptance
of the disease, optimized self-management and a reduced number
of psychological barriers towards better disease control [5-7]. In
this initiative, the psychology team will provide support to the
other health care professionals at SDCO and its partner hospitals
to improve their understanding and management of patients
with psychologic challenges in relation to their diabetes. Further,
to provide individual psychologic intervention to patients with
psychologic problems and challenges in relation to their diabetes,
and finally develop this psychologic program to patients.
Screening for Diabetic Complications Package: The screening
for diabetic complications is traditionally offered on different
appointments and by different specialists on different days. In this
initiative screening for all complications is done at the same day
in one location. Thus, the patient meets in the out-patient clinic at
SDCO and have blood and urine samples taken, ECG (patients older
than 65 years). Thereafter, the patient goes to the optometrist to
have a fundus-photo and an optical coherence tomography taken.
The pictures will be send to an ophthalmologist for immediate
evaluation and description. The patient goes to the podiatrist to
have a foot examination, counseling and risk evaluation. Finally the
patient is seen by the endocrinologist, who takes care of collection
and evaluation of all results, give advice, change or optimize the
pharmacologic treatment if needed, and plan for future treatment
and visits. The whole screening package takes approximately 2½
hours for the patient.
Screening and Treatment of Diabetic Autonomous
Neuropathy: The prevalence and incidence of diabetic complication
varies and is reduced by improving glycemic control in both type 1
and type 2 diabetes [8,9]. Autonomous neuropathy is related to the
diabetes duration. In this initiative, patients with neuropathy and
suspected gastroparesis is referred to a thorough and structured
workup involving both the endocrinologist and gastroenterologist,
and including both endoscopy and ventricular motility tests, before
eventually treatment.
Screening and Treatment of Patients with Concomitant
Renal Insufficiency: Patients with diabetes complicated with
diabetic kidney disease have an increased morbidity and mortality.
Optimal treatment of this group of patients seems to require
a team-based management approach [10]. Evidence suggests
that multidisciplinary consultations with an endocrinologist,
nephrologist and diabetes nurse together may improve renal
outcomes in these patients [11] and that increased focus on
multifactorial intervention improves long-term renal outcomes
[12]. In the future multidisciplinary out-patient clinic at SDCO,
patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less
than 30 ml/min, or between 30 and 40 ml/min and concomitant
complications like acidosis, anemia, hypertension or calciumphosphate
problems, will be referred to this team. Patients with
progressive proteinuria will also have this opportunity.
Courses for Patients with Recurrent Ketoacidosis or Severe
Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia is associated with an increased risk
of hospital admission, falls and accidents in patients with diabetes.
It can have significant physical and mental consequences and is
the most important limiting factor in yielding and maintaining
good glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes [13]. New
technology such as continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGM)
can have a significant effect of reducing severe hypoglycemia in
patients, in particular patients with hypoglycemia unawareness.
It seems that by combining CGM by focused and structured
patient education do have the best outcome in minimizing the
risk of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes and
hypoglycemia unawareness [14]. A multidisciplinary group-based
patient education program with a diabetes nurse, endocrinologist,
psychologist and dietician will educate and empower the patient
to improve skills in order to prevent and avoid future severe
hypoglycemic events. The family of the patient is included in
this program, and the sessions will focus on: theory, fear of
hypoglycemia, coping of unawareness, insulin adjustments, physical
activity, carbohydrates and glucose sensors. These sessions can be
combined with individual counseling.
Diabetes Screening and Assistance from Diabetes Team
in Other Departments: Many patients admitted to the hospital
for other somatic reasons such as cardiovascular disease, surgery,
neurological disease and infectious diseases also have diabetes,
particularly type 2 diabetes. Specialists and nurses at these
departments do not always have the necessary skills and focus on
care and treatment of patients with diabetes. Studies have shown
that implementation of a specialized team of diabetes nurses
supervised by an endocrinologist providing assistance to other
departments at the hospital, can have a positive impact in reducing
the length of hospitalization stay, and an increased satisfaction for
both patient and health care professionals at the department [15-
17]. The aim of the initiative at SDCO is three-fold: optimization of
care and treatment for all patients with diabetes admitted to the
hospitals regardless of the department, a systematic opportunistic
screening of patients with unknown diabetes by HbA1c, and
to develop and improve the skills and competences in diabetes
management of the health care professionals at all departments
of the hospital. Thus, in all departments where an opportunistic
screening for diabetes is considered relevant based on the
characteristics of the population, all patients will at the time of
admittance have a blood sample taken to be analyzed for HbA1c. In
patients with unknown diabetes who have an increased HbA1c ≥ 48
mmol/mol, will have this re-tested and if confirmed, the specialized
diabetes team will be involved to evaluate and manage the patient.
The diabetes nurse will provide assistance to all patients with known diabetes where the department requests assistance and
help in diabetes management. The team from SDCO will provide
continuous training and regular theme-based courses for the health
care professionals at these departments.
As an add-on to the above described initiative, a project
including a clinical pharmacist intervention is considered. Recent
studies suggest that a pharmacist-driven medication review,
patient interview and follow-up in patients admitted to the acute
admission ward may reduce the rate of readmissions and emergency
department visits in these patients [18]. The proposed project is to
include a clinical pharmacist to intervene in all in-patients who have
significant pharmacologic treatment changes during the hospital
admission. The intervention will include a medication review and
evaluation, a patient motivational interview and follow-up with the
primary health care sector after discharge from hospital.
Diabetes Screening and Assistance from Diabetes Team
in Psychiatric Departments: The patients with diabetes and
psychiatric co-morbidities constitute a particular challenge.
Psychiatric patients have a two- to four-fold increased prevalence
of diabetes and the metabolic syndrome compared to the general
population. Patients with severe psychiatric diseases and diabetes
have a significant increased mortality [19]. As previously described
studies of admitted patients with somatic disease support the impact
of a specialized diabetes team providing assistance to departments
[15-17]. In this initiative, a specialized nurse-based diabetes
team will provide assistance to health care professionals at the
psychiatric departments and in the regional out-patient psychiatric
clinics, in the management and care of patients with diabetes. As for
the non-psychiatric departments, the team from SDCO will provide
continuous training and regular theme-based courses for the health
care professionals at the psychiatric departments. The diabetes
nurse in this initiative will be supervised by an endocrinologist.
Advice before Pregnancy: Fertile women with diabetes have
an increased risk of giving birth to a child with malformations and
pregnancy complications if their glycemic control is not optimized
before conception. Optimized glycemic control before and during
pregnancy reduces the risk for diabetic complications, severe
hypoglycemia, preterm delivery, macrosomia and malformations
and neonatal hypoglycemia. In this initiative women with a wish
of pregnancy in the near future and having either type 1 or type
2 diabetes and ethnicity other than Danish are offered a program
with multidisciplinary advice covering adjustment of medicine,
co-morbidity, goal of treatment, injection technique, blood glucose
measurement, carbohydrate counting, vitamin supplements and
complication screening. This program will be provided by the
endocrinologist, diabetes nurse and dietician. In addition the
women are offered a group-based program covering planning of
pregnancy and follow-up during and after pregnancy.
Start-Up Course for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 1
Diabetes: For patients with type 1 diabetes previous studies show
that intensively treated patients have a significant better long-term
outcome with a reduced incidence of microvascular complications
[9] and cardiovascular disease [20]. Many barriers towards
optimized glycemic control can be identified such as risk and fear for
hypoglycemia, insufficient knowledge of long-term consequences
of the disease, acceptance problems and social challenges. Thus,
it is of decisive importance that management of the patient with
newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes is well-structured, thorough and
individualized. At SDCO newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes patients
will be followed in a 6 months ‘start-up package’ which will
comprise a multidisciplinary team course and patient interviews,
individualized and group-based, covering all elements of treatment,
self-management and social significance for the patient and their
relatives. The structured course will be supplemented by videos
and e-learning to support empowerment and ‘living the good life
with diabetes’ in these patients.
Preparation before Surgery
Patients with diabetes who are planned for surgery may have
an increased risk of complications during or after surgery. Studies
have shown that the risk of deep infections postoperatively is
increased in patients with a high level of HbA1c [21], an increased
risk of infections, infarctions and reduced survival is linked to
perioperative hyperglycemia [22], and patients with an HbA1c
above 70 mmol/mol who underwent cardiovascular surgery was
found to have up to a four-fold risk of mortality [23]. A recent
study found that initiating and optimizing basal insulin therapy in
patients planned for cardiac surgery resulted in fewer infections
postoperatively and a shorter hospitalization stay [24]. In this
initiative, type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients treated with insulin are
offered referral to SDCO for evaluation and optimization of insulin
treatment before planned surgery. The patient will be evaluated by
an endocrinologist, diabetes nurse and dietician at SDCO. Focus for
evaluation, treatment and advice will be to: optimize insulin therapy
and antihypertensive treatment if needed, patient advice regarding
precautions related to diabetes management perioperatively, and an
individualized diet plan if needed. Patients planned for orthopedic
and gastrointestinal surgery will be included in this initiative.
Children and Adolescents with Diabetes
As listed in Table 1, the approved initiatives for children and
adolescents with type 1 diabetes resembles those planned for adult
patients with diabetes as previously described. The education
programs, theme-based meetings and start-up courses will be
adapted to the age-group (pre-school age, school-age below 15
years and school-age above 15 years) and adjusted to the special
needs and challenges in these patients. The initiative concerning
a diabetes psychologist will be distinctively different from the
initiative for adults. Thus, it will comprise of systematic screening
and evalulation of children and adolescents with diabetes, groupbased
therapy if needed, intervention using the acceptance and
commitment therapy (ACT) method, psycho-education sessions
for patients and their families, and training and supervision to the
health care professionals.
Planned Initiatives in Near Future at SDCO Awaiting
Approval: The future initiatives in pipeline are listed on Table 2.
The initiatives will cover both clinical and non-clinical initiatives
and for both adults, children and adolescents with various forms
of diabetes. The non-clinical initiatives are meant to support future management and treatment of patients, including the new
clinical initiatives. Thus, a unit for the evaluation of new technology,
research and development will guide the use of new technology
to the right patients in order to benefit most patients taken costbenefit
analyses into consideration as well. A unit for quality and
follow-up will provide surveillance of key quality indicators of the
patients treated at SDCO and of patients treated elsewhere in the
Region of Southern Denmark, and will improve quality of patient
management by providing data on the patient population and at
the individual level. A mutual model for the evaluation of the above
initiatives will be developed and described.
Table 2: Planned future clinical and non-clinical initiatives from the Steno Diabetes Center Odense for patients with diabetes.

The future clinical initiatives await at present to be described
in detail. These initiatives will elaborate and extend the already
approved initiatives. Multidisciplinary out-patient clinics for
patients with diabetes with concomitant rheumatic, cardiac,
odontological disease and other chronic diseases are in pipeline.
A package for screening of diabetes complications in one day is in
pipeline covering type 2 diabetes patients who are followed in the
primary health care sector by the primary health care provider,
as well as extended follow-up of patients with former gestational
diabetes after delivery, and a nurse-based call center for health
care professionals and patients followed in the primary health care
sector in the Region of Southern Denmark.
Cross-Sectorial Collaboration and Development of
Competences and Skills: Hand-in-hand with the above
described initiatives a thorough and structured cross-sectorial
collaboration between SDCO, partner hospitals, communities and
the primary health care providers is currently being developed
and implemented. This includes a structured and ongoing training
program and theme-based courses for all health care professionals
who is taken care of patients with diabetes, in order to further
develop and improve competences and skills.
Patient Involvement in the Organization and Clinical
Decision-Making at SDCO: Involvement of patients with diabetes
and their relatives are considered important at SDCO. It is assumed
that involvement in the clinical process can facilitate transformation
of knowledge and improve empowerment provided by the health
care professionals. Further, the diabetes educators and health care
professionals can better adapt and target education, treatment
and care to the needs and resources of the individual patient.
User involvement at SDCO will focus on both organization (patient
board, committees, involvement in new developments etc.), and on
individual patient care. Thus, involvement is planned widespread
on different relevant areas as: standard patient care, new
clinical initiatives, cross-sectorial collaboration, development of
competences and skills and clinical research. A patient committee
consisting of 15 diabetes patients and relatives of different age,
gender, diabetes type, social and educational background has been
established. The main purpose with this patient committee is to
collaborate with and give advice to the management and health
care professionals at the center concerning the future strategy. This
in order to ensure that current activities and new clinical initiatives
are in agreement with the needs and wishes from patients with diabetes, their relatives and families in the future.
Summary and Conclusions
The overall vision of the new initiatives originating from Steno
Diabetes Center Odense and by potential dissemination to the whole
Region of Southern Denmark embracing both the primary and
secondary health care sector, is to normalize lifetime expectancy
and quality of life in people with diabetes. By improving all areas of
diabetes management, treatment, care and patient selfcare, it may
be possible to avoid or minimize future complications in patients
with diabetes irrespective of type of diabetes or concomitant
disease. The new and forthcoming clinical and non-clinical
initiatives will potentially help to fulfil this goal.
For more Lupine Publishers Open access journals please visit our website
For more Diabetes open access journal please click here
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/lupine_online
Tuesday, September 17, 2019
Lupine Publishers: About Lupine Publishers
Lupine Publishers: About Lupine Publishers: About Lupine Publishers Lupine Publishers is one of the world’s largest open access publisher of peer-reviewed, fully peer reviewe...
Friday, September 13, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | A Combined Material Substituti...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | A Combined Material Substituti...: Lupine Publishers | Journal of Textile and Fashion Designing Abstract This paper empirically presents a batik produ...
Thursday, September 12, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Congenital Craniofacial and Ce...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Congenital Craniofacial and Ce...: Lupine Publishers | Journal of Otolaryngology Abstract Congenital cysts, sinuses and fistulas of the head and neck are ano...
Wednesday, September 11, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Green Revolution as Technologi...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Green Revolution as Technologi...: Lupine Publishers- Environmental and Soil Science Abstract The beginning of Human being’s effort to meet the need f...
Tuesday, September 10, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | The Elemental Composition of S...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | The Elemental Composition of S...: Lupine Publishers- Environmental and Soil Science Annotation Studying the macro- and microelement composition of the...
Friday, September 6, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Sub-Soil Properties of Hydrocarbon Contaminated Si...
Lupine Publishers: Sub-Soil Properties of Hydrocarbon Contaminated Si...: Lupine Publishers- Environmental and Soil Science Abstract This study aims at assessing the subsurface soil properties of conta...
Wednesday, September 4, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Effect of Environment on Secon...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Effect of Environment on Secon...: Lupine Publishers- Environmental and Soil Science Abstract Medicinal plants constitute main resource base of almost all...
Tuesday, September 3, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Forced Traction: An Error
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Forced Traction: An Error: Lupine Publishers | Journal of Veterinary Science Introduction Immediate cause of dystocia requires certain preparations an...
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Lupine Publishers| Semaglutide versus liraglutide for treatment of obesity
Lupine Publishers| Journal of Diabetes and Obesity Abstract Background: Once weekly (OW) semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide...

-
Lupine Publishers| Journal of Diabetes and Obesity Abstract Background: Once weekly (OW) semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide...
-
Stem Cell Therapy in Diabetes Mellitus by Poondy Gopalratnam Raman in Archives of Diabetes & Obesity in Lupine Publishers Di...
-
Lupine Publishers| Journal of Diabetes and Obesity Abstract A recent study using next-generation RNA sequencing was reported on g...